Select the properties of the sn2 reaction mechanism. – Select the properties of the SN2 reaction mechanism, a fundamental concept in organic chemistry, unveils the intricacies of nucleophilic substitution reactions. This mechanism, characterized by its bimolecular nature and inversion of configuration, plays a pivotal role in the synthesis of complex organic compounds.
Delve into the defining characteristics, influencing factors, stereochemical implications, and practical applications of the SN2 reaction mechanism, gaining a comprehensive understanding of its significance in organic chemistry.
The SN2 reaction mechanism, a cornerstone of nucleophilic substitution reactions, offers a unique perspective on the reactivity and selectivity of organic compounds. Its distinctive features, including the inversion of configuration and the dependence on substrate, nucleophile, and leaving group, provide valuable insights into the behavior of organic molecules.
By exploring the intricacies of the SN2 reaction mechanism, chemists can harness its power for the targeted synthesis of desired organic compounds.
Nucleophilic Substitution (SN2) Reaction Mechanism: Select The Properties Of The Sn2 Reaction Mechanism.

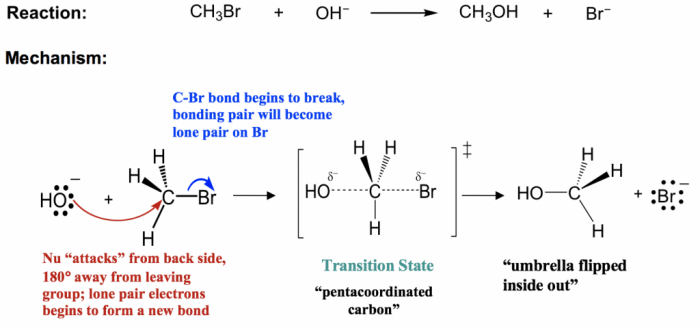
Key Characteristics of SN2 Reactions
- Second-order reaction: Rate depends on both the nucleophile and substrate concentrations.
- Stereochemical inversion: The configuration of the substrate’s stereocenter is inverted.
- Unimolecular transition state: The transition state involves the substrate and the nucleophile only.
- Strong nucleophiles and weak bases: Nucleophiles that are strong bases tend to be poor SN2 nucleophiles.
- Polar aprotic solvents: SN2 reactions are favored in polar aprotic solvents, which stabilize the transition state.
Factors Affecting SN2 Reactivity, Select the properties of the sn2 reaction mechanism.
Substrate Structure
- Primary substrates react faster than secondary and tertiary substrates due to steric hindrance.
- Electron-withdrawing groups on the substrate increase the rate of SN2 reactions by stabilizing the transition state.
Nucleophile Strength
- Stronger nucleophiles react faster in SN2 reactions.
- Nucleophiles with negative charges or lone pairs of electrons are generally stronger.
Leaving Group Ability
- Good leaving groups (e.g., halides) promote SN2 reactions by stabilizing the transition state.
- Weak leaving groups (e.g., hydroxide) hinder SN2 reactions by forming a more stable starting material.
Stereochemistry of SN2 Reactions
Inversion of Configuration
- In SN2 reactions, the nucleophile attacks the substrate from the opposite side of the leaving group, resulting in inversion of configuration.
- This is due to the concerted nature of the reaction, where the nucleophile and leaving group break and form bonds simultaneously.
Applications of SN2 Reactions
Organic Synthesis
- SN2 reactions are used to prepare a variety of organic compounds, including alcohols, ethers, and amines.
- They are particularly useful for introducing specific functional groups into organic molecules.
Comparison with Other Nucleophilic Substitution Mechanisms
SN2 vs. SN1 Reactions
| Characteristic | SN2 | SN1 |
|---|---|---|
| Rate law | Second-order | First-order |
| Stereochemistry | Inversion | Racemization or carbocation rearrangement |
| Mechanism | Concerted | Two-step (carbocation formation followed by nucleophilic attack) |
| Substrate | Primary, secondary, tertiary | Tertiary (primary and secondary substrates give carbocations) |
Helpful Answers
What is the key characteristic of the SN2 reaction mechanism?
The SN2 reaction mechanism is characterized by its bimolecular nature, meaning that the rate-determining step involves the collision of two molecules: the substrate and the nucleophile.
How does the SN2 reaction mechanism affect the stereochemistry of the product?
The SN2 reaction mechanism results in the inversion of configuration at the reaction center, meaning that the stereochemistry of the product is opposite to that of the starting material.
What factors influence the reactivity of the SN2 reaction?
The reactivity of the SN2 reaction is influenced by the structure of the substrate, the strength of the nucleophile, and the ability of the leaving group.