Hhmi the eukaryotic cell cycle and cancer answers – In the realm of cell biology, HHMI’s groundbreaking research on the eukaryotic cell cycle and cancer has illuminated the intricate mechanisms underlying cellular life and disease. This exploration unveils the fundamental processes that govern cell division, the checkpoints that ensure its fidelity, and the ways in which cancer cells evade these safeguards to proliferate uncontrollably.
As we delve into this captivating topic, we will uncover the key stages of the eukaryotic cell cycle, the regulatory checkpoints that orchestrate its progression, and the disruptions that can lead to cell cycle abnormalities. We will also examine the role of cancer cells in disrupting these checkpoints and the genetic mutations that drive their uncontrolled growth.
Finally, we will highlight HHMI’s invaluable contributions to this field and explore the promising avenues of future research that hold the potential to revolutionize cancer treatment.
1. The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle

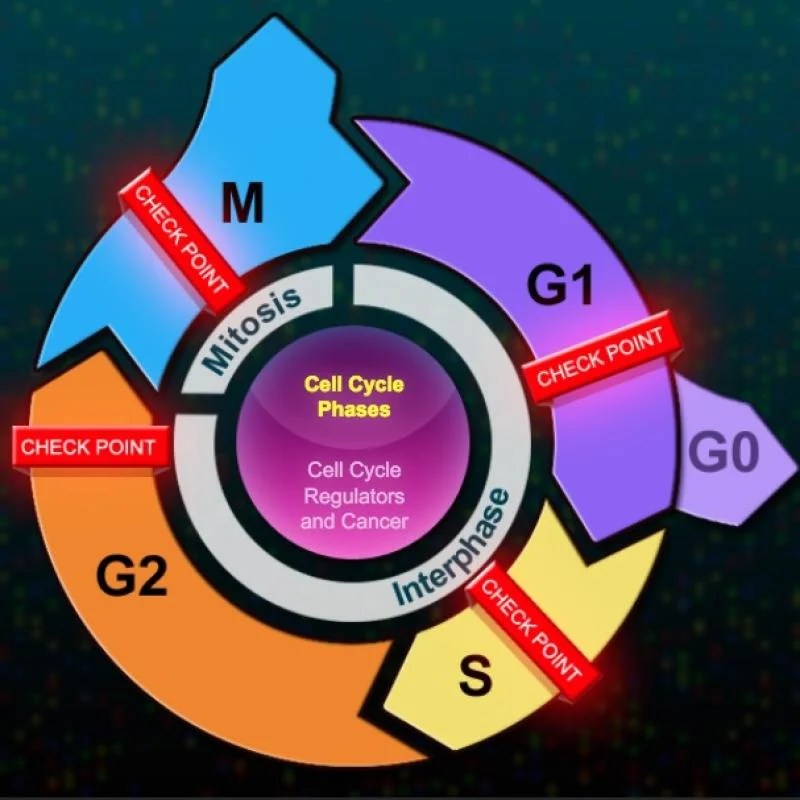
The eukaryotic cell cycle is a complex process that ensures the accurate duplication and distribution of genetic material during cell division. It consists of four distinct stages:
- Interphase:The longest phase, where the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for division.
- Prophase:Chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase:Chromosomes align along the metaphase plate.
- Anaphase:Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase:Two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes, and the cell divides into two daughter cells.
The cell cycle is regulated by a series of checkpoints that ensure the accurate completion of each stage before the next one can begin. These checkpoints are:
- G1 checkpoint:Ensures that the cell is ready to enter S phase by checking for DNA damage and sufficient nutrients.
- S phase checkpoint:Ensures that DNA replication is complete and accurate before the cell enters G2 phase.
- G2 checkpoint:Ensures that the cell is ready to enter mitosis by checking for DNA damage and proper chromosome alignment.
- M checkpoint:Ensures that all chromosomes are properly aligned before anaphase begins.
Disruptions to the cell cycle can lead to a variety of problems, including:
- Cell death:If the cell cycle is disrupted too severely, the cell may die.
- Cancer:If the cell cycle is disrupted in a way that allows cells to divide uncontrollably, cancer can result.
- Developmental abnormalities:If the cell cycle is disrupted during embryonic development, it can lead to birth defects.
2. Cancer and the Cell Cycle
Cancer cells are characterized by their ability to evade the checkpoints of the cell cycle, allowing them to divide uncontrollably. This can be caused by a variety of mutations, including:
- Mutations in checkpoint proteins:These mutations can prevent the checkpoints from functioning properly, allowing cells to progress through the cell cycle even if they are damaged or have not completed DNA replication.
- Mutations in oncogenes:Oncogenes are genes that promote cell division. Mutations in these genes can lead to the overexpression of proteins that drive the cell cycle forward, even in the absence of proper checkpoints.
- Mutations in tumor suppressor genes:Tumor suppressor genes are genes that inhibit cell division. Mutations in these genes can lead to the loss of their function, allowing cells to divide uncontrollably.
The cell cycle is a key target for cancer treatment. By targeting the cell cycle, it is possible to prevent cancer cells from dividing and multiplying. There are a variety of drugs that target different stages of the cell cycle, including:
- CDK inhibitors:These drugs inhibit the activity of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), which are enzymes that drive the cell cycle forward.
- DNA-damaging agents:These drugs damage DNA, which can trigger the cell cycle checkpoints and lead to cell death.
- Microtubule inhibitors:These drugs inhibit the formation of microtubules, which are essential for cell division.
3. HHMI’s Contributions to the Understanding of the Cell Cycle and Cancer: Hhmi The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle And Cancer Answers

HHMI has been a major contributor to the understanding of the cell cycle and cancer. HHMI-funded researchers have made a number of important discoveries, including:
- The identification of the checkpoints of the cell cycle:HHMI-funded researchers were among the first to identify the checkpoints of the cell cycle and to understand their role in preventing cancer.
- The discovery of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes:HHMI-funded researchers have made major contributions to the discovery of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, which are key players in cancer development.
- The development of new cancer treatments:HHMI-funded researchers have developed a number of new cancer treatments that target the cell cycle, including CDK inhibitors and DNA-damaging agents.
HHMI’s research has had a major impact on the development of cancer treatments. HHMI-funded researchers have developed a number of new drugs that are now used to treat cancer, and their research has led to a better understanding of how cancer cells grow and divide.
This knowledge has helped to improve the lives of cancer patients and has led to new hope for a cure.
4. Future Directions for Research
There are a number of areas of future research on the cell cycle and cancer, including:
- The development of new cancer treatments:There is a need for new cancer treatments that are more effective and have fewer side effects. HHMI-funded researchers are working to develop new drugs that target the cell cycle and to improve the delivery of these drugs to cancer cells.
- The identification of new biomarkers for cancer:Biomarkers are molecules that can be used to identify cancer cells and to track the progress of cancer treatment. HHMI-funded researchers are working to identify new biomarkers that can be used to improve the diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
- The development of new strategies for preventing cancer:There is a need for new strategies for preventing cancer, especially among high-risk populations. HHMI-funded researchers are working to develop new vaccines and other preventive measures that can help to reduce the incidence of cancer.
The cell cycle is a complex and dynamic process that is essential for life. HHMI-funded researchers are working to understand the cell cycle and to develop new ways to treat cancer. This research has the potential to improve the lives of cancer patients and to lead to new hope for a cure.
Clarifying Questions
What is the eukaryotic cell cycle?
The eukaryotic cell cycle is a series of precisely regulated stages that a cell undergoes during its growth and division. It consists of four main phases: G1, S, G2, and M.
How do cancer cells evade cell cycle checkpoints?
Cancer cells often acquire mutations that allow them to bypass or inactivate cell cycle checkpoints. This enables them to continue proliferating even when there are DNA damage or other abnormalities.
What are some examples of HHMI’s contributions to the understanding of the cell cycle and cancer?
HHMI scientists have made significant discoveries about the molecular mechanisms that control the cell cycle and how they are disrupted in cancer. They have also developed new technologies for studying these processes and identified potential targets for cancer therapy.