One of a gene pair crossword – Embark on a captivating crossword puzzle journey into the realm of gene pairs, where alleles dance and inheritance patterns unfold. Prepare to unravel the secrets of dominant, recessive, and co-dominant traits as we delve into the fascinating world of genetics.
From the basics of gene pairs to the intricacies of homozygous and heterozygous genotypes, this crossword puzzle will test your knowledge and expand your understanding of the fundamental principles of inheritance.
Definition of “One of a Gene Pair”
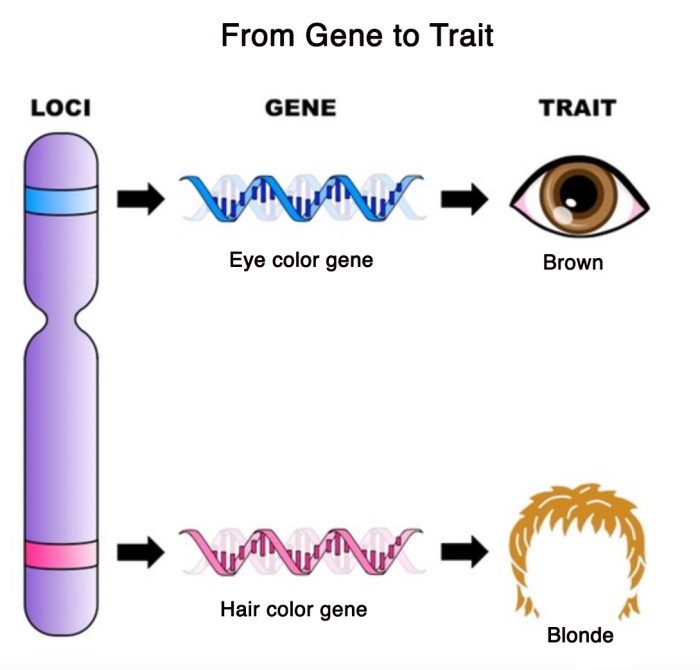
Genes are segments of DNA that code for specific traits. Each gene has two copies, one inherited from each parent. These copies are called alleles. Alleles can be identical or different. When alleles are different, the individual is said to be heterozygous for that gene.
When alleles are identical, the individual is said to be homozygous for that gene.
One of a gene pair refers to one of the two alleles that an individual has for a particular gene. For example, if a gene codes for eye color, an individual could have two alleles for brown eyes or one allele for brown eyes and one allele for blue eyes.
Examples of Gene Pairs and Alleles
Here are some examples of gene pairs and their corresponding alleles:
- Eye color:Brown, blue, green, hazel
- Hair color:Black, brown, blonde, red
- Blood type:A, B, AB, O
- Sickle cell anemia:Normal allele, sickle cell allele
- Cystic fibrosis:Normal allele, cystic fibrosis allele
Types of Gene Pairs
Gene pairs can be classified into different types based on their interaction and the resulting phenotype. The three main types of gene pairs are dominant-recessive, co-dominant, and incompletely dominant.
Dominant-Recessive Gene Pairs, One of a gene pair crossword
In dominant-recessive gene pairs, one allele is dominant and masks the expression of the other recessive allele. The dominant allele is represented by an uppercase letter, while the recessive allele is represented by a lowercase letter. For example, in the case of the gene pair for flower color in pea plants, the dominant allele (P) codes for purple flowers, while the recessive allele (p) codes for white flowers.
If a pea plant inherits two dominant alleles (PP), it will have purple flowers. If it inherits one dominant allele and one recessive allele (Pp), it will also have purple flowers because the dominant allele masks the expression of the recessive allele.
However, if a pea plant inherits two recessive alleles (pp), it will have white flowers.
Co-Dominant Gene Pairs
In co-dominant gene pairs, both alleles are fully expressed in the phenotype. This means that neither allele is dominant or recessive. For example, in the case of the gene pair for blood type in humans, the allele for type A blood (IA) is co-dominant with the allele for type B blood (IB).
If you’re struggling with a crossword puzzle clue about “one of a gene pair,” you might find some helpful tips in the Kumon Level L Test Answers . These resources provide a comprehensive overview of genetics and can help you solve even the most challenging crossword puzzles.
With a little practice, you’ll be able to conquer any crossword clue related to one of a gene pair.
If a person inherits one allele for type A blood and one allele for type B blood, they will have type AB blood, which is a combination of both type A and type B antigens.
Incomplete Dominance Gene Pairs
In incompletely dominant gene pairs, neither allele is fully dominant, and the phenotype is a blend of the two alleles. For example, in the case of the gene pair for flower color in snapdragons, the allele for red flowers (R) is incompletely dominant to the allele for white flowers (r).
If a snapdragon inherits one allele for red flowers and one allele for white flowers, it will have pink flowers, which is a blend of red and white.
Inheritance Patterns
Inheritance patterns refer to the manner in which genetic traits are passed down from parents to offspring. In the context of gene pairs, the inheritance patterns depend on the dominance relationship between the alleles within the pair.
Dominant and Recessive Alleles
In a gene pair, one allele may be dominant over the other. A dominant allele masks the expression of the recessive allele, meaning that the dominant trait will be observed in the offspring even if they carry only one copy of the dominant allele.
A recessive allele, on the other hand, is only expressed when two copies of the allele are present in the offspring’s genotype.
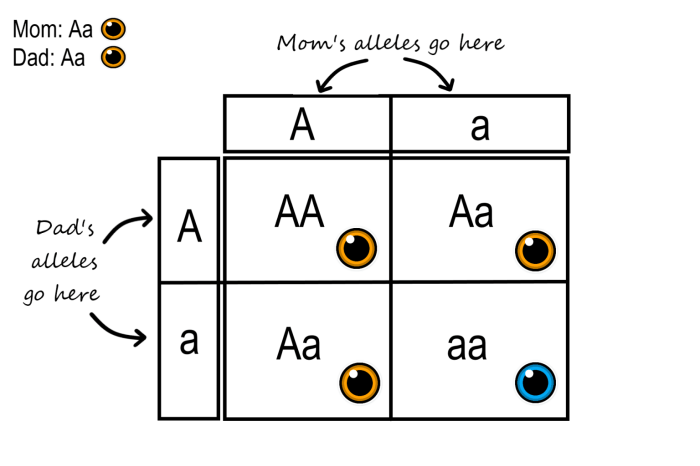
Punnett Square
A Punnett square is a tool used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of their parents. To construct a Punnett square, the alleles of each parent are listed along the sides of the square, and the possible combinations of alleles are represented in the boxes.
For example, consider a gene pair where one allele (A) is dominant over the other (a). If one parent has the genotype Aa and the other parent has the genotype aa, the Punnett square would look like this:
| A | a | |
|---|---|---|
| a | Aa | aa |
| a | Aa | aa |
The Punnett square shows that the possible genotypes of the offspring are Aa (50%) and aa (50%). Since the A allele is dominant, all offspring will have the dominant phenotype (expressed trait), regardless of whether they carry one or two copies of the dominant allele.
Phenotype and Genotype
The phenotype of an organism is its observable characteristics, such as its physical appearance, behavior, and biochemical properties. The genotype of an organism is its genetic makeup, which is determined by the alleles it inherits from its parents.
The genotype of a gene pair determines the phenotype of an organism by controlling the production of proteins. Proteins are the building blocks of cells and tissues, and they play a role in all aspects of an organism’s development and function.
The specific proteins that are produced by a gene pair are determined by the alleles that make up the pair.
Examples of Phenotypes and Genotypes
In humans, the gene pair for eye color has two alleles: one for brown eyes and one for blue eyes. A person who inherits two brown eye alleles will have brown eyes. A person who inherits two blue eye alleles will have blue eyes.
A person who inherits one brown eye allele and one blue eye allele will have hazel eyes.
The gene pair for height has many different alleles, each of which codes for a different height. A person who inherits two tall alleles will be tall. A person who inherits two short alleles will be short. A person who inherits one tall allele and one short allele will be of average height.
Homozygous and Heterozygous: One Of A Gene Pair Crossword
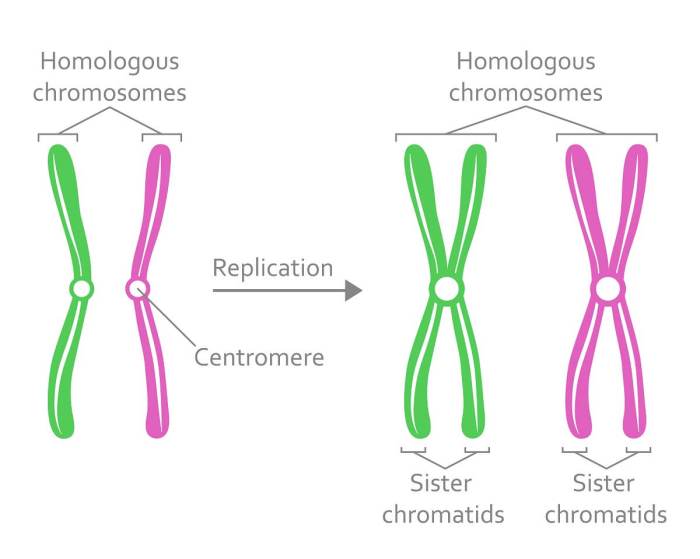
In genetics, understanding the concepts of homozygous and heterozygous is crucial. These terms describe the makeup of an individual’s genes, which determine their traits and characteristics.
Homozygous
An individual is homozygous for a particular gene when they possess two identical copies of that gene. This means that both copies of the gene have the same alleles, which are different versions of the gene. For example, if a gene controls eye color and one allele codes for brown eyes while the other codes for blue eyes, an individual who is homozygous for brown eyes will have two copies of the brown eye allele.
Heterozygous
In contrast, an individual is heterozygous for a gene when they possess two different copies of that gene. This means that one copy of the gene has one allele, while the other copy has a different allele. Using the same eye color example, an individual who is heterozygous for eye color will have one copy of the brown eye allele and one copy of the blue eye allele.
The homozygous and heterozygous states have important implications for the expression of traits. Homozygous individuals will always express the trait associated with the allele they possess two copies of, while heterozygous individuals may express either the dominant or recessive trait, depending on the specific gene and alleles involved.
FAQ Overview
What is a gene pair?
A gene pair consists of two copies of the same gene, one inherited from each parent.
What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous genotypes?
Homozygous genotypes have two identical alleles for a particular gene, while heterozygous genotypes have two different alleles.